Introduction
Mobile applications and web applications are two distinct categories of software that cater to different user needs and scenarios. In this comparison, we'll explore the key differences between these two types of applications to help you make informed decisions for your projects or businesses.
Descriptions of Mobile and Web Applications:

Mobile applications (often referred to as "apps") are software programs specifically designed to run on mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. These applications are typically available for download and installation from dedicated app stores, such as the Apple App Store for iOS devices and Google Play Store for Android devices.

Web applications, on the other hand, are software programs accessible through web browsers on various devices, including desktop computers, laptops, smartphones, and tablets. Unlike mobile apps, web applications do not require installation from an app store and are accessed directly via a web address (URL).
Platform Specificity VS Cross-Platform Compatibility:
Mobile applications are platform-specific, meaning they are developed separately for different operating systems like iOS and Android. This necessitates dedicated development efforts for each platform, increasing development time and costs. In contrast, web applications are accessible through web browsers on a wide range of devices and operating systems, making them a cost-effective choice for reaching a broader audience.
Performance and User Experience:
Mobile apps are designed to offer an optimized user experience on the device they are installed on. They take full advantage of the device's hardware, ensuring superior performance. Mobile apps are ideal for scenarios where responsiveness, speed, and device-specific features are critical. Web applications, while versatile, may not provide the same level of performance due to their reliance on web browsers. However, they compensate with cross-device accessibility. If you already know how to create cool designs for web and mobile apps welcome to our "Find No Code Job" page
Offline Functionality VS Internet Dependency:
Mobile apps excel in providing offline functionality. They can store data locally on the device, allowing users to access content and features even without an internet connection. This feature is invaluable for applications that need to function seamlessly in remote or low-connectivity environments. On the other hand, web applications typically require an internet connection to operate optimally. Some web apps may offer limited offline functionality through data caching, but they are inherently internet-dependent.
App Store Distribution VS Direct Access:
As said in the description, mobile apps are distributed through app stores such as the Apple App Store and Google Play Store. These stores provide a controlled environment for users to discover, download, and update applications securely. In contrast, web applications are accessed directly via a web address (URL), eliminating the need for installation. Users can access web apps instantly without going through an app store, reducing friction.
Cost and Development Considerations:

Developing mobile apps for multiple platforms can be costlier and more time-consuming due to the need for separate development efforts. Web applications, with their cross-platform compatibility, offer a more cost-effective approach, as a single codebase can serve users on various devices and operating systems. This cost efficiency can be a significant advantage for businesses with budget constraints.
Conclusion
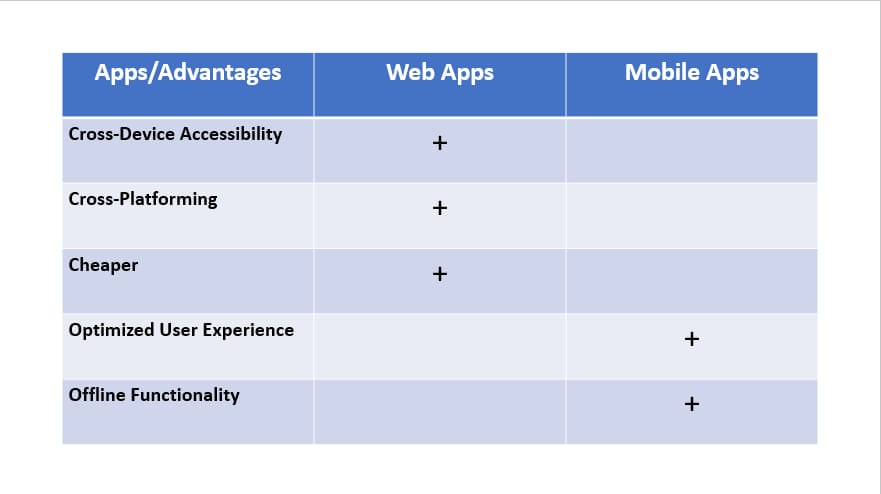
In summary, mobile applications and web applications have their distinct strengths and weaknesses. Mobile apps shine in providing optimized performance, access to device hardware, and robust offline functionality. They are well-suited for tasks that require top-notch user experiences on specific platforms. Web applications, on the other hand, excel in cross-platform compatibility, cost-effective development, and ease of access. They are a versatile choice for reaching a broad user base without the need for platform-specific development. The choice between the two depends on your project's goals, target audience, and budget. Understanding these differences is essential for making the right decision and delivering the best user experience.
Also check our another article about The 6 Best No-Code App Builders In 2024







